Why Modern Living Needs the Ancient Wisdom of Brahmasthan
The Sacred Center: Technical Guidelines for Brahmasthan in Modern Architecture
The Brahmasthan the energetic heart of traditional Indian architecture is no longer just a philosophical concept. Modern building science now provides precise technical standards to measure, validate, and implement these ancient principles in contemporary construction. This comprehensive guide bridges millennia-old spatial wisdom with cutting-edge environmental measurement, offering architects, builders, and homeowners a scientifically-backed framework for creating harmonious living spaces.
Understanding Brahmasthan Through Scientific Measurement
The Brahmasthan operates on multiple measurable parameters that directly impact human health, comfort, and well-being. Recent research in environmental building science has validated many traditional Vastu principles through quantifiable metrics.
Core Technical Standards
Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Requirements
- Standard: <0.5 milligauss (mG)
- Rationale: Minimal electromagnetic interference supports optimal cellular function and neurological balance
- Measurement: Tri-axis gaussmeter at multiple times and load conditions
Energy Quality Assessment
- Standard: 8,000-12,000 Bovis Units (BU)
- Rationale: Positive life force energy correlation with occupant vitality and wellness
- Measurement: Bovis biometer or calibrated L-rod systems
Geometric Precision
- Standard: ±2-10 cm measurement accuracy (application dependent)
- Rationale: Precise center calculation ensures optimal energy distribution
- Tools: Digital measuring tape, laser measurement, GPS coordinates
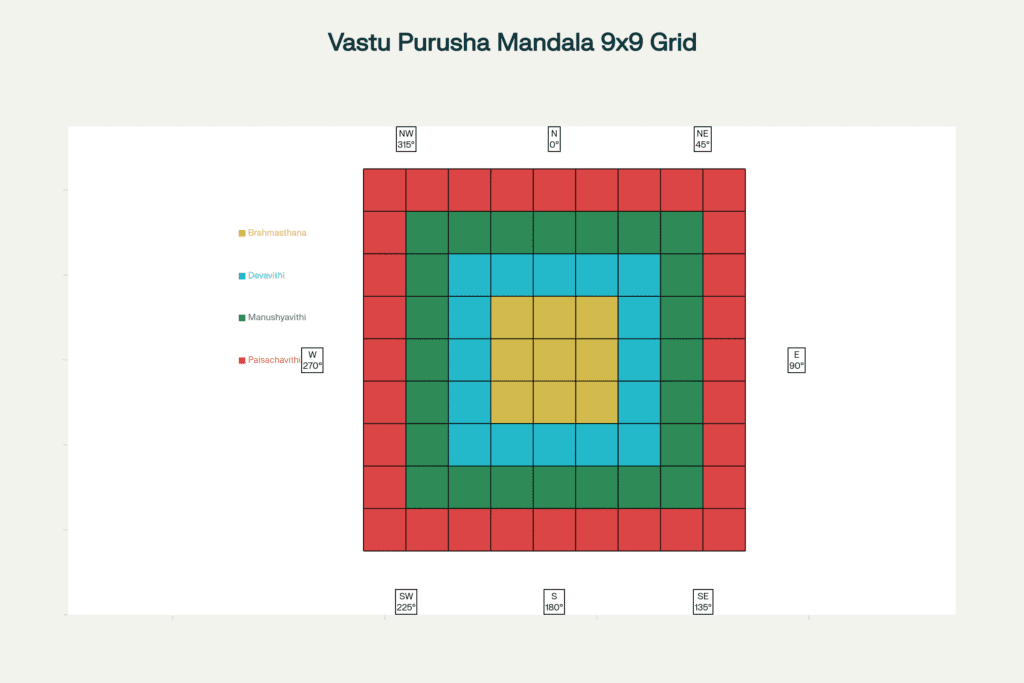
The Vastu Purusha Mandala: Technical Implementation
The 9×9 grid system (81 squares total) provides the mathematical framework for Brahmasthan placement and energy zone allocation.
Grid System Specifications
Central Void Requirements
- Standard: 3×3 squares minimum (11% of total floor area)
- Purpose: Unobstructed energy circulation and natural light/air distribution
- Tolerance: ±1% area variation acceptable
Directional Alignment
- Standard: ±1° magnetic north accuracy
- Tools: Magnetic compass, GPS orientation, surveyor's equipment
- Critical: Maintains cosmic orientation and seasonal solar optimization
Environmental Parameters for Optimal Brahmasthan
Beyond traditional measurements, modern Brahmasthan design incorporates comprehensive environmental monitoring to ensure occupant health and comfort.
| Parameter | Standard Value | Measurement Tool | Critical For | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Field (EMF) | <0.5 mG | Tri-axis Gaussmeter | Health & EMF sensitivity | Zero tolerance |
| Bovis Energy Units | 8,000-12,000 BU | Bovis Biometer/L-Rod | Energy quality & wellness | ±500 BU acceptable |
| Measurement Precision | ±2-10 cm | Digital measuring tape/Laser | Geometric accuracy | Context dependent |
| Grid System | 9×9 Vastu Purusha Mandala | Compass & Grid overlay | Traditional alignment | Must be precise |
| Central Void Area | 3×3 squares (11% minimum) | Area calculation software | Energy circulation | ±1% area variation |
| Directional Accuracy | ±1° magnetic alignment | Magnetic compass/GPS | Cosmic orientation | Very strict |
| Optimal Room Temperature | 22-26°C (72-79°F) | Digital thermometer | Comfort & productivity | ±2°C acceptable |
| Air Quality Index | 0-50 (Good to Excellent) | Air quality monitor | Respiratory health | ±10 points acceptable |
| Humidity Range | 40-60% RH | Hygrometer | Material preservation | ±5% acceptable |
| Sound Level | <40 dB | Sound level meter | Peace & concentration | ±5 dB acceptable |
| Natural Light Level | 300-500 lux | Lux meter | Circadian rhythm | ±50 lux acceptable |
| Floor Area Ratio | 0.8-1.2 maximum | Architectural plans | Space utilization | ±0.1 acceptable |
Climate Control Standards
Temperature Optimization
- Range: 22-26°C (72-79°F)
- Impact: Supports metabolic efficiency and cognitive function
- Tolerance: ±2°C variation acceptable
Humidity Management
- Range: 40-60% relative humidity
- Benefits: Prevents mold growth, preserves materials, maintains respiratory health
- Monitoring: Digital hygrometers with data logging
Air Quality Maintenance
- Standard: 0-50 AQI (Good to Excellent)
- Parameters: PM2.5, CO2, VOCs, formaldehyde levels
- Tools: Multi-parameter air quality monitors
Electromagnetic Field Management
Modern homes contain numerous EMF sources that can disrupt the Brahmasthan's energy balance. Technical EMF management is crucial for maintaining the center's beneficial properties.
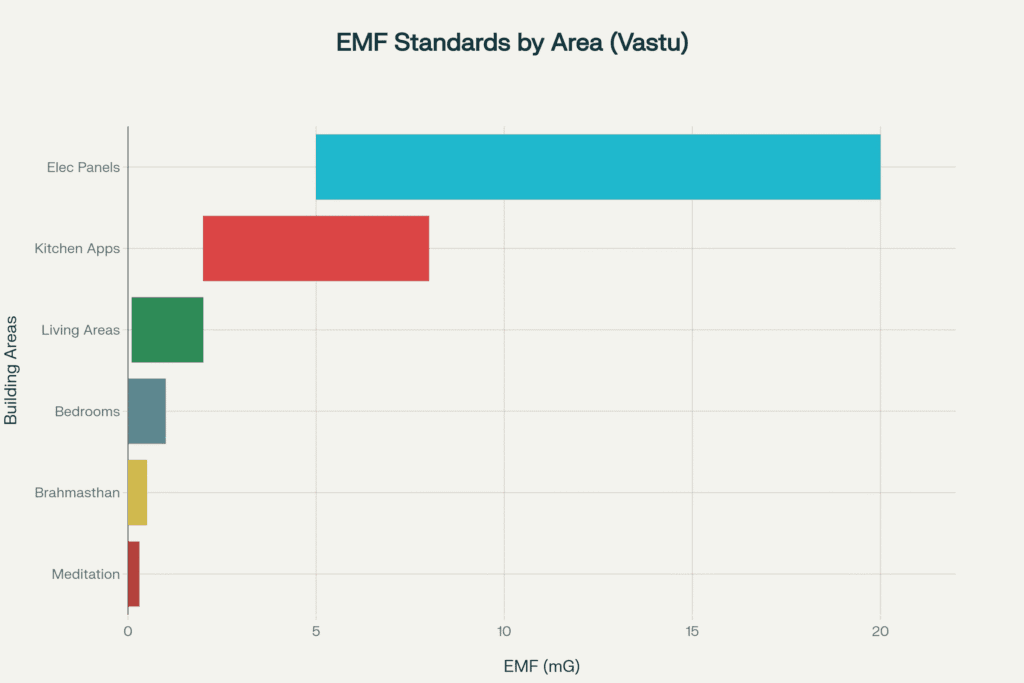
EMF Source Control
High-Risk Areas to Avoid
- Electrical panels and distribution boxes (5-20 mG typical)
- Kitchen appliances and motors (2-8 mG)
- WiFi routers and electronic devices (variable)
Optimal Placement Strategy
- Southeast zone: Main electrical systems and panels
- Avoid center: No electrical infrastructure in central 3×3 grid
- Northeast protection: Minimal EMF sources in meditation/study areas
Energy Measurement Protocols
Scientific validation of Brahmasthan effectiveness requires systematic measurement and documentation.
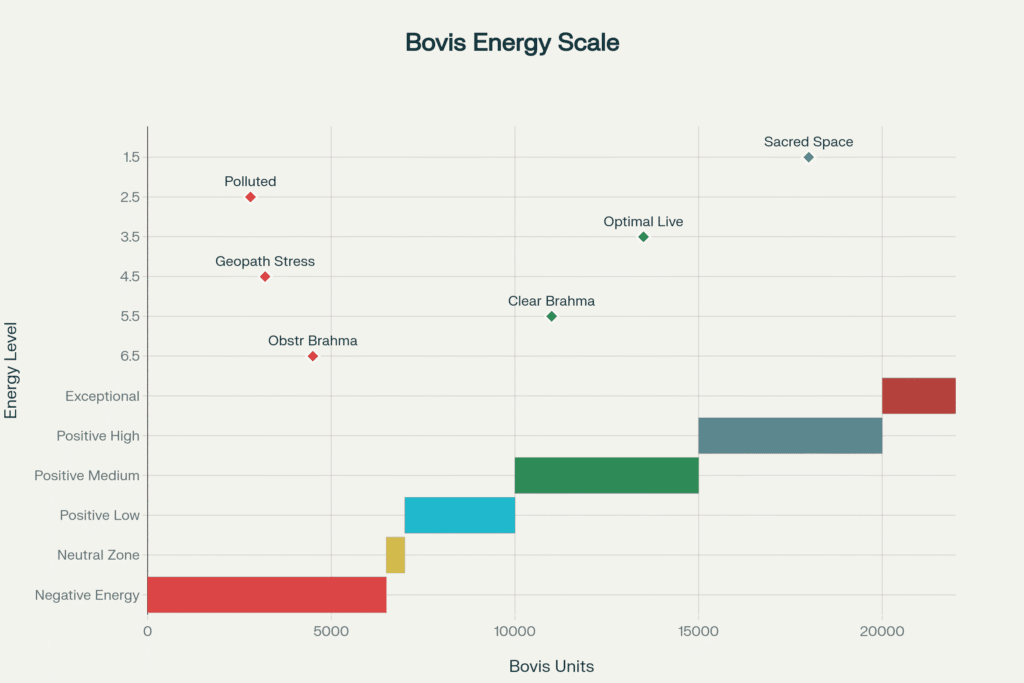
Bovis Energy Scale Application
Measurement Categories
- Negative Energy: 0-6,500 BU (harmful, requires remediation)
- Neutral Zone: 6,500-7,000 BU (minimal impact)
- Positive Energy: 7,000+ BU (beneficial for habitation)
- Optimal Brahmasthan: 8,000-12,000 BU (highly beneficial)
Factors Affecting Energy Readings
- Geopathic stress patterns
- Underground water veins
- Electromagnetic interference
- Structural materials and orientation
- Seasonal and lunar variations
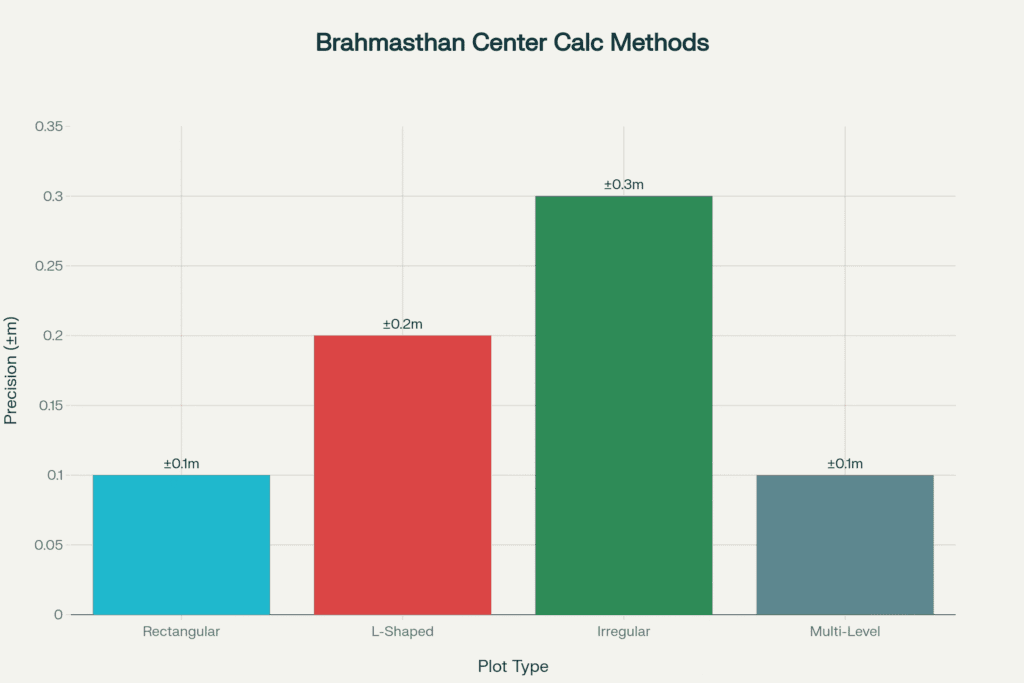
Mathematical Calculation Methods
Precise Brahmasthan location requires sophisticated geometric calculations adapted to various architectural configurations.
Plot-Specific Calculations
Rectangular Buildings
- Method: Diagonal intersection
- Formula: Center = ((x₁+x₂)/2, (y₁+y₂)/2)
- Accuracy: ±2 cm for residential, ±1 cm for sacred architecture
Irregular Layouts
- Method: Center of mass calculation
- Process: Divide into triangles, calculate weighted centroids
- Software: CAD programs with centroid calculation tools
Multi-Story Buildings
- Method: Vertical projection from ground floor center
- Considerations: Structural changes, MEP risers, floor-to-floor variations
- Tolerance: ±10 cm maximum deviation per floor
Measurement Tools and Equipment
Professional Brahmasthan assessment requires precision instruments capable of detecting subtle environmental variations.
Essential Measurement Kit
Electromagnetic Detection
- Tri-axis gaussmeter (±0.1 mG accuracy)
- RF spectrum analyzer for high-frequency detection
- Ground potential meter for electrical safety
Energy Assessment
- Bovis biometer or dowsing rods
- Pendulum for directional confirmation
- Lecher antenna for frequency-specific detection
Environmental Monitoring
- Digital thermometer/hygrometer
- Air quality meter (PM2.5, CO2, VOCs)
- Sound level meter for acoustic assessment
- Lux meter for natural light measurement
Implementation in Modern Construction
Integrating Brahmasthan principles into contemporary building practices requires careful coordination across all design and construction phases.
Design Phase Integration
Architectural Planning
- Establish 9×9 grid overlay early in schematic design
- Secure central void in structural, MEP, and interior packages
- Coordinate with building codes and accessibility requirements
Structural Considerations
- Avoid columns within central 3×3 grid
- Span beams around center or use continuous ceiling to minimize visual impact
- Implement uniform load distribution around perimeter
MEP System Integration
- Route major electrical panels to Southeast zone
- Avoid plumbing and HVAC equipment in central area
- Design natural ventilation to enhance airflow through center
Construction Quality Control
Measurement Verification
- GPS survey of site boundaries and center point
- Construction layout verification at each floor level
- Final as-built confirmation of center location
Environmental Testing
- Baseline EMF readings before electrical installation
- Progressive monitoring during construction phases
- Final commissioning with full environmental assessment
Remediation Strategies for Existing Buildings
When ideal Brahmasthan conditions cannot be achieved due to existing construction constraints, specific technical interventions can restore energy balance.
Electromagnetic Mitigation
Passive Shielding
- Conductive mesh or paint in critical areas
- Strategic placement of EMF-absorbing materials
- Grounding system optimization
Active Solutions
- Electronic field cancellation systems
- Power line filters and surge protection
- Dedicated circuits for sensitive areas
Structural Adaptations
Visual Remedies
- Continuous false ceiling to minimize beam impact
- Light-colored finishes to enhance luminosity
- Strategic mirror placement for space expansion
Functional Modifications
- Lightweight, moveable furniture systems
- Hidden storage solutions in perimeter walls
- Flexible lighting design with multiple control zones
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Professional Brahmasthan implementation requires systematic documentation and ongoing monitoring to ensure long-term effectiveness.
Documentation Standards
Pre-Construction Records
- Site survey with GPS coordinates
- Baseline environmental measurements
- Geological and hydrological assessment
Construction Monitoring
- Progress photos with measurement verification
- Material certification and EMF testing
- MEP system commissioning reports
Post-Completion Validation
- Comprehensive environmental assessment
- Energy measurement mapping
- Occupant comfort and wellness tracking
Ongoing Maintenance Protocols
Annual Assessments
- EMF level verification
- Air quality and comfort parameter testing
- Structural integrity and alignment confirmation
Seasonal Adjustments
- Lighting system optimization for solar changes
- HVAC calibration for seasonal comfort
- Furniture arrangement for optimal energy flow
Research and Future Applications
Emerging technologies and scientific understanding continue to validate and expand traditional Brahmasthan principles.
Advanced Measurement Technologies
Quantum Field Detection
- Consciousness-field interaction measurement
- Quantum coherence assessment in living spaces
- Bio-resonance testing for occupant compatibility
Smart Building Integration
- IoT sensor networks for continuous monitoring
- AI-driven optimization based on environmental data
- Predictive maintenance using energy pattern analysis
Health and Wellness Correlation
Biometric Monitoring
- Heart rate variability in different zones
- Sleep quality correlation with room placement
- Stress hormone level tracking in occupants
Longitudinal Studies
- Multi-year occupant health tracking
- Productivity and cognitive performance assessment
- Chronic condition improvement documentation
Conclusion
The scientific validation of Brahmasthan principles through modern measurement and analysis provides unprecedented opportunities to create built environments that actively support human health and well-being. By integrating ancient spatial wisdom with contemporary building science, architects and builders can design homes and buildings that function as living systems responsive, adaptive, and inherently supportive of human flourishing.
The technical standards outlined in this guide offer a practical framework for implementing these principles in modern construction, ensuring that the profound insights of traditional Vastu Shastra continue to enhance human habitation in the 21st century and beyond.
Technical Specifications Summary
Core Standards:
- Optimal Brahmasthan EMF: <0.5 mG
- Ideal Bovis Energy Range: 8,000-12,000 BU
- Measurement Precision: ±2-10 cm depending on application
- Grid System: 9×9 Vastu Purusha Mandala (81 squares)
- Central Void: 3×3 squares minimum (11% of total area)
- Directional Accuracy: ±1° for magnetic alignment
This technical analysis integrates traditional Vastu wisdom with modern scientific measurement and validation methods, providing a comprehensive framework for implementing Brahmasthan principles in contemporary architecture.

